本文由风听雨声授权原创发布
EventBus 是一个面向Android和Java的开源库,使用发布者/订阅者模式实现松散耦合,简化组件之间的通信。使用简单,效率高,体积小。具备高级特性,如传递线程、订阅优先级等,下面是官方的EventBus原理图
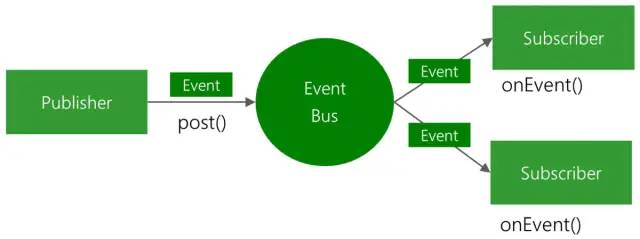
EventBus原理图.png
本文将对EventBus(基于当前EventBus最新版本3.2.0)进行详细的源码分析,会有比较详细的代码注释,本文将从以下方面进行展开
基本使用简单介绍
Subscribe注解
注册和订阅事件
取消注册
发送事件
处理事件
粘性事件
Annotation的使用方式
手写核心代码
基本使用
注册
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
取消注册
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
发送事件
EventBus.getDefault().post("event");
接收事件
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN)public void subscribeMethod(String event){
}
Subscribe注解
@Documented@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface Subscribe {
ThreadMode threadMode() default ThreadMode.POSTING;
boolean sticky() default false;
int priority() default 0;
}
运行时作用于方法的注解,注解的value有以下3个
1.threadMode():接收事件的线程,默认POSTING,和发送事件同一线程
2.sticky():是否为粘性事件,默认false
3.priority():接收事件优先级,默认0,即默认所有事件相同优先级
ThreadMode接收事件的线程
public enum ThreadMode { POSTING,
MAIN,
MAIN_ORDERED,
BACKGROUND,
ASYNC
}
ThreadMode有以下5种
1.POSTING:将在发布事件的同一线程中直接调用订阅者。这是默认设置。事件交付意味着开销最少,因为它完全避免了线程切换。
2.MAIN:*在Android上,订阅者将在Android的主线程(UI线程)中被调用。如果发布线程是主线程、订阅方方法将被直接调用,阻塞发布线程。
3.MAIN_ORDERED:在Android上,订阅者将在Android的主线程(UI线程)中被调用。与MAIN不同的是事件将一直排队等待交付。这确保了post调用是非阻塞的。
4.BACKGROUND:在Android上,订阅者将在后台线程中被调用。如果发布线程不是主线程,订阅方方法将在发布线程中直接调用。如果发布线程是主线程,则EventBus使用后台线程,它将按顺序交付所有事件。
5.ASYNC:订阅将在一个单独的线程中被调用。总是独立于发布线程和主线程。
注册和订阅事件
getDefault(),双重判断加锁的单例
public static EventBus getDefault() { EventBus instance = defaultInstance;
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (EventBus.class) {
instance = EventBus.defaultInstance;
if (instance == null) {
instance = EventBus.defaultInstance = new EventBus();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
Builder设计模式,传入默认Builder
public EventBus() { this(DEFAULT_BUILDER);
}
EventBus(EventBusBuilder builder) {
logger = builder.getLogger();
subscriptionsByEventType = new HashMap<>();
typesBySubscriber = new HashMap<>();
stickyEvents = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
mainThreadSupport = builder.getMainThreadSupport();
mainThreadPoster = mainThreadSupport != null ? mainThreadSupport.createPoster(this) : null;
backgroundPoster = new BackgroundPoster(this);
asyncPoster = new AsyncPoster(this);
indexCount = builder.subscriberInfoIndexes != null ? builder.subscriberInfoIndexes.size() : 0;
subscriberMethodFinder = new SubscriberMethodFinder(builder.subscriberInfoIndexes,
builder.strictMethodVerification, builder.ignoreGeneratedIndex);
logSubscriberExceptions = builder.logSubscriberExceptions;
logNoSubscriberMessages = builder.logNoSubscriberMessages;
sendSubscriberExceptionEvent = builder.sendSubscriberExceptionEvent;
sendNoSubscriberEvent = builder.sendNoSubscriberEvent;
throwSubscriberException = builder.throwSubscriberException;
eventInheritance = builder.eventInheritance;
executorService = builder.executorService;
}
默认Builder参数初始值
public class EventBusBuilder { private final static ExecutorService DEFAULT_EXECUTOR_SERVICE = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
boolean logSubscriberExceptions = true;
boolean logNoSubscriberMessages = true;
boolean sendSubscriberExceptionEvent = true;
boolean sendNoSubscriberEvent = true;
boolean throwSubscriberException;
boolean eventInheritance = true;
boolean ignoreGeneratedIndex;
boolean strictMethodVerification;
ExecutorService executorService = DEFAULT_EXECUTOR_SERVICE;
List<Class<?>> skipMethodVerificationForClasses;
List<SubscriberInfoIndex> subscriberInfoIndexes;
Logger logger;
MainThreadSupport mainThreadSupport;
EventBusBuilder() {
}
注册
获取订阅的class对象
2.根据订阅的class对象,解析订阅方法Subscribe注解,并封装成SubscriberMethod,加入到
List<SubscriberMethod>集合
处理事件
public void register(Object subscriber) { Class<?> subscriberClass = subscriber.getClass();//1
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = subscriberMethodFinder.findSubscriberMethods(subscriberClass);//2
synchronized (this) {
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods) {
subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod);//3
}
}
}
findSubscriberMethods(Class<?> subscriberClass)
1.从缓存中取,有直接返回
findUsingInfo(subscriberClass)和findUsingReflection(subscriberClass),两者都是通过反射解析Subscribe,findUsingInfo比findUsingReflection多了FindState的对象池
3.subscriberMethods加入缓存,以便第二次打开不再需要反射解析
List<SubscriberMethod> findSubscriberMethods(Class<?> subscriberClass) { //先从缓存的Map<Class<?>, List<SubscriberMethod>> METHOD_CACHE ,key为注册的class对象,value为List<SubscriberMethod>
List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = METHOD_CACHE.get(subscriberClass);
if (subscriberMethods != null) {
return subscriberMethods;
}
if (ignoreGeneratedIndex) {//是否每次都从反射去拿方法参数 , 默认为false
subscriberMethods = findUsingReflection(subscriberClass);
} else {
//默认走这个方法
subscriberMethods = findUsingInfo(subscriberClass);
}
if (subscriberMethods.isEmpty()) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriberClass
+ " and its super classes have no public methods with the @Subscribe annotation");
} else {
//缓存起来,以便第二次打开缓存如果直接返回
METHOD_CACHE.put(subscriberClass, subscriberMethods);
return subscriberMethods;
}
}
private List<SubscriberMethod> findUsingInfo(Class<?> subscriberClass) {
//第一次打开相当于 FindState findState = new FindState()
FindState findState = prepareFindState();
//initForSubscriber方法做了以下3点
//this.subscriberClass = clazz = subscriberClass;
// skipSuperClasses = false;
//subscriberInfo = null;
findState.initForSubscriber(subscriberClass);
while (findState.clazz != null) { //这里相当于subscriberClass != null
findState.subscriberInfo = getSubscriberInfo(findState);
//在这里相当于findState.subscriberInfo = null 会走else
if (findState.subscriberInfo != null) {
SubscriberMethod[] array = findState.subscriberInfo.getSubscriberMethods();
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : array) {
if (findState.checkAdd(subscriberMethod.method, subscriberMethod.eventType)) {
findState.subscriberMethods.add(subscriberMethod);
}
}
} else {
////将Subscribe 注解上的参数封装成 SubscriberMethod 添加到 findState.subscriberMethods List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods
findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(findState);
}
findState.moveToSuperclass();
}
//return封装好的 annotation 参数ArrayList<subscriberMethods>
return getMethodsAndRelease(findState);
}
通过反射解析参数,已加上比较详细的注释
private void findUsingReflectionInSingleClass(FindState findState) {
Method[] methods;
try {
// 获取register的class对象的所有方法,包括私有和抽象
methods = findState.clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
} catch (Throwable th) {
// Workaround for java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError, see https://github.com/greenrobot/EventBus/issues/149
try {
methods = findState.clazz.getMethods();
} catch (LinkageError error) { // super class of NoClassDefFoundError to be a bit more broad...
String msg = "Could not inspect methods of " + findState.clazz.getName();
if (ignoreGeneratedIndex) {
msg += ". Please consider using EventBus annotation processor to avoid reflection.";
} else {
msg += ". Please make this class visible to EventBus annotation processor to avoid reflection.";
}
throw new EventBusException(msg, error);
}
findState.skipSuperClasses = true;
}
for (Method method : methods) {
int modifiers = method.getModifiers();
//筛选public方法,且没有static abstract.. 等等修饰符
if ((modifiers & Modifier.PUBLIC) != 0 && (modifiers & MODIFIERS_IGNORE) == 0) {
//获取方法参数的class
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterTypes.length == 1) {//方法参数数目为1,方法参数大于1不走
//获取方法上Subscribe注解
Subscribe subscribeAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(Subscribe.class);
if (subscribeAnnotation != null) {
//方法参数的class 只有一个,即 parameterTypes[0]
Class<?> eventType = parameterTypes[0];
if (findState.checkAdd(method, eventType)) {//true
ThreadMode threadMode = subscribeAnnotation.threadMode();//获取将Subscribe Annotation的threadMode
//将Subscribe 注解上的参数封装成 SubscriberMethod 添加到 findState.subscriberMethods List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods
findState.subscriberMethods.add(new SubscriberMethod(method, eventType, threadMode,
subscribeAnnotation.priority(), subscribeAnnotation.sticky()));
}
}
//strictMethodVerification 是否验证参数 抛异常 默认为false
} else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) {
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();
throw new EventBusException("@Subscribe method " + methodName +
"must have exactly 1 parameter but has " + parameterTypes.length);
}
} else if (strictMethodVerification && method.isAnnotationPresent(Subscribe.class)) {
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();
throw new EventBusException(methodName +
" is a illegal @Subscribe method: must be public, non-static, and non-abstract");
}
}
}
处理事件
1.优先级排序
处理粘性事件
private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) { //方法参数class
Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType;
// Subscription (register的class subscriber,注解参数subscriberMethod)
Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
//subscriptionsByEventType HashMap<方法参数Class<?>, CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription>>
//Subscription (register的class subscriber,注解参数subscriberMethod)
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);
if (subscriptions == null) {
subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions);
} else {
if (subscriptions.contains(newSubscription)) {
throw new EventBusException("Subscriber " + subscriber.getClass() + " already registered to event "
+ eventType);
}
}
//subscriptions.size() == register了eventBus 的class 所有接受 event的方法数目
int size = subscriptions.size();
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) {
//根据priority 优先级排序
subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription);
break;
}
}
//typesBySubscriber HashMap key register EventBus 的 class value subscribedEvents<方法参数的class>
List<Class<?>> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);
if (subscribedEvents == null) {
subscribedEvents = new ArrayList<>();
typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents);
}
//方法参数的class
subscribedEvents.add(eventType);
if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {//处理粘性事件
//把一个Event发送到一个还没有初始化的Activity/Fragment,即尚未订阅事件。
// 那么如果只是简单的post一个事件,那么是无法收到的,这时候,就需要用到粘性事件
if (eventInheritance) {//默认为true
Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet();
//stickyEvents = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) {
Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey();
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) {
Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue();
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);//如果有粘性事件 注册时就执行
}
}
} else {
Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType);
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
}
小结一下
注册和订阅事件已经走完了,这里主要是EventBus的实例化,并将订阅方法Subscribe注解解析,封装成List<SubscriberMethod> findSubscriberMethods。
*取消注册
避免内存泄漏
public synchronized void unregister(Object subscriber) {
List<Class<?>> subscribedTypes = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);
if (subscribedTypes != null) {
for (Class<?> eventType : subscribedTypes) {
unsubscribeByEventType(subscriber, eventType);
}
typesBySubscriber.remove(subscriber);
} else {
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "Subscriber to unregister was not registered before: " + subscriber.getClass());
}
}
private void unsubscribeByEventType(Object subscriber, Class<?> eventType) {
List<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);
if (subscriptions != null) {
int size = subscriptions.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Subscription subscription = subscriptions.get(i);
if (subscription.subscriber == subscriber) {
subscription.active = false;
subscriptions.remove(i);
i--;
size--;
}
}
}
}
发送事件
public void post(Object event) { //利用ThreadLocal将PostingThreadState线程安全
PostingThreadState postingState = currentPostingThreadState.get();
List<Object> eventQueue = postingState.eventQueue;
//将事件加入 eventQueue -> ArrayList<Object>
eventQueue.add(event);
if (!postingState.isPosting) {
postingState.isMainThread = isMainThread();
postingState.isPosting = true;
if (postingState.canceled) {
throw new EventBusException("Internal error. Abort state was not reset");
}
try {
while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) {
//发送事件 eventObject 对象
postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0), postingState);
}
} finally {
postingState.isPosting = false;
postingState.isMainThread = false;
}
}
}
private void postSingleEvent(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState) throws Error {
//eventObject对象的class
Class<?> eventClass = event.getClass();
boolean subscriptionFound = false;
if (eventInheritance) {//默认为true
List<Class<?>> eventTypes = lookupAllEventTypes(eventClass);
int countTypes = eventTypes.size();
for (int h = 0; h < countTypes; h++) {
Class<?> clazz = eventTypes.get(h);
subscriptionFound |= postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, clazz);
}
} else {
subscriptionFound = postSingleEventForEventType(event, postingState, eventClass);
}
if (!subscriptionFound) {
if (logNoSubscriberMessages) {
logger.log(Level.FINE, "No subscribers registered for event " + eventClass);
}
if (sendNoSubscriberEvent && eventClass != NoSubscriberEvent.class &&
eventClass != SubscriberExceptionEvent.class) {
post(new NoSubscriberEvent(this, event));
}
}
}
private boolean postSingleEventForEventType(Object event, PostingThreadState postingState, Class<?> eventClass) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions;
synchronized (this) {
subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventClass);
}
if (subscriptions != null && !subscriptions.isEmpty()) {
for (Subscription subscription : subscriptions) {
postingState.event = event;
postingState.subscription = subscription;
boolean aborted;
try {
postToSubscription(subscription, event, postingState.isMainThread);
aborted = postingState.canceled;
} finally {
postingState.event = null;
postingState.subscription = null;
postingState.canceled = false;
}
if (aborted) {
break;
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
处理事件和发送事件
根据当前线程和订阅的ThreadMode决定怎么发送事件
private void postToSubscription(Subscription subscription, Object event, boolean isMainThread) { switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) {
case POSTING://相同线程 直接反射调用
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
break;
case MAIN://主线程
//MainThreadSupport - >isMainThread() -> looper == Looper.myLooper();
if (isMainThread) {//判断当前是否是主线程 ,主线程直接反射调用
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
} else {
//new HandlerPoster .enqueue() handler切换主线程 send
mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
}
break;
case MAIN_ORDERED://主线程有序 利用handler + eventBus 自己实现的 PendingPostQueue
if (mainThreadPoster != null) {
mainThreadPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
} else {
// temporary: technically not correct as poster not decoupled from subscriber
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
break;
case BACKGROUND://子线程
if (isMainThread) {//当前是主线程 newCachedThreadPool线程池执行
backgroundPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
} else {//不是主线程 直接执行
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
break;
case ASYNC://异步 newCachedThreadPool线程池执行
asyncPoster.enqueue(subscription, event);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);
}
}
粘性事件
应用场景
我们要把一个Event发送到一个还没有初始化的Activity/Fragment,即尚未订阅事件。那么如果只是简单的post一个事件,那么是无法收到的,这时候,就需要用到粘性事件,它可以帮我们解决这类问题。使用方式
1.使用粘性事件时需要调用粘性注册方法注册
2.订阅方法声明粘性事件粘性事件原理
粘性事件发送时会将粘性事件存起来,当有类注册方式为粘性注册,那么就会检查类中有没有粘性订阅方法,如果有,直接invoke发送事件。
if (subscriberMethod.sticky) {//处理粘性事件 //把一个Event发送到一个还没有初始化的Activity/Fragment,即尚未订阅事件。
// 那么如果只是简单的post一个事件,那么是无法收到的,这时候,就需要用到粘性事件
if (eventInheritance) {//默认为true
Set<Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object>> entries = stickyEvents.entrySet();
//stickyEvents = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry<Class<?>, Object> entry : entries) {
Class<?> candidateEventType = entry.getKey();
if (eventType.isAssignableFrom(candidateEventType)) {
Object stickyEvent = entry.getValue();
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);//如果有粘性事件 注册时就执行
}
}
} else {
Object stickyEvent = stickyEvents.get(eventType);
checkPostStickyEventToSubscription(newSubscription, stickyEvent);
}
}
- Annotation的使用方式
前面分析了运用反射的使用方式和源码,这是默认的实现,如果项目中有大量的订阅事件的方法,会对项目运行时的性能产生一定的影响。其实除了在项目运行时通过反射查找订阅事件的方法信息,查找订阅事件方法信息的方式,生成一个辅助的索引类来保存这些信息,和编译时注解-ButterKnife框架原理分析及手写 原理类似。
基本使用
这里我为了方便修改和注释内部源码,直接将EventBus clone下来引入
implementation project(path: ':EventBus')
annotationProcessor project(path: ':EventBusAnnotationProcessor')
android {
defaultConfig {
javaCompileOptions {
annotationProcessorOptions {
// 指定辅助索引类的名称和包名
arguments = [ eventBusIndex : 'com.ftys.eventbusdemo.EventBusIndex' ]
}
}
}
Application中调用
EventBus.builder().addIndex(new EventBusIndex()).installDefaultEventBus();
生成的索引类结构如下
public class EventBusIndex implements SubscriberInfoIndex { private static final Map<Class<?>, SubscriberInfo> SUBSCRIBER_INDEX;
static {
SUBSCRIBER_INDEX = new HashMap<Class<?>, SubscriberInfo>();
putIndex(new SimpleSubscriberInfo(MainActivity.class, true, new SubscriberMethodInfo[] {
new SubscriberMethodInfo("subscribeMethod", String.class, ThreadMode.MAIN),
}));
}
private static void putIndex(SubscriberInfo info) {
SUBSCRIBER_INDEX.put(info.getSubscriberClass(), info);
}
@Override
public SubscriberInfo getSubscriberInfo(Class<?> subscriberClass) {
SubscriberInfo info = SUBSCRIBER_INDEX.get(subscriberClass);
if (info != null) {
return info;
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
手写EventBus核心代码
public class EventBus { private static volatile EventBus mInstance;
private List<SubscriberMethod> subscriberMethods = new ArrayList<>();
private final Map<Class<?>, CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription>> subscriptionsByEventType;
private final Map<Object, List<Class<?>>> typesBySubscriber;
private Executor executor;
private EventBus() {
subscriptionsByEventType = new HashMap<>();
typesBySubscriber = new HashMap<>();
executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
}
public static EventBus getDefault() {
if (mInstance == null) {
synchronized (EventBus.class) {
if (mInstance == null) {
mInstance = new EventBus();
}
}
}
return mInstance;
}
public void register(Object subscriber) {
Class<?> registerClass = subscriber.getClass();
Method[] methods = registerClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
Subscribe subscribe = method.getAnnotation(Subscribe.class);
if (subscribe != null) {
Class<?>[] parameterClasses = method.getParameterTypes();
if (parameterClasses.length == 1) {
SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod = new SubscriberMethod(method, parameterClasses[0],
subscribe.threadMode(), subscribe.priority(), subscribe.sticky());
if (!subscriberMethods.contains(subscriberMethod)) {
subscriberMethods.add(subscriberMethod);
}
}
}
}
for (SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod : subscriberMethods) {
subscribe(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
}
}
private void subscribe(Object subscriber, SubscriberMethod subscriberMethod) {
Class<?> eventType = subscriberMethod.eventType;
Subscription newSubscription = new Subscription(subscriber, subscriberMethod);
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);
if (subscriptions == null) {
subscriptions = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
subscriptionsByEventType.put(eventType, subscriptions);
}
int size = subscriptions.size();
for (int i = 0; i <= size; i++) {
if (i == size || subscriberMethod.priority > subscriptions.get(i).subscriberMethod.priority) {
//根据priority 优先级排序
subscriptions.add(i, newSubscription);
break;
}
}
//typesBySubscriber HashMap key register EventBus 的 class value subscribedEvents<方法参数的class>
List<Class<?>> subscribedEvents = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);
if (subscribedEvents == null) {
subscribedEvents = new ArrayList<>();
typesBySubscriber.put(subscriber, subscribedEvents);
}
//方法参数的class
subscribedEvents.add(eventType);
}
private List<Object> eventQueueOut = new ArrayList<>();
public void post(Object event) {
List<Object> eventQueue = eventQueueOut;
eventQueue.add(event);
while (!eventQueue.isEmpty()) {
//发送事件 eventObject 对象
postSingleEvent(eventQueue.remove(0));
}
}
private void postSingleEvent(Object event) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<Subscription> subscriptions;
synchronized (this) {
subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(event.getClass());
}
if (subscriptions != null && !subscriptions.isEmpty()) {
for (Subscription subscription : subscriptions) {
postToSubscription(subscription, event);
}
}
}
private void postToSubscription(final Subscription subscription, final Object event) {
boolean isMainThread = (Looper.myLooper() == Looper.getMainLooper());
switch (subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode) {
case POSTING://相同线程 直接反射调用
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
break;
case MAIN://主线程
//MainThreadSupport - >isMainThread() -> looper == Looper.myLooper();
if (isMainThread) {//判断当前是否是主线程 ,主线程直接反射调用
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
} else {
Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
});
}
break;
case MAIN_ORDERED://主线程有序 利用handler + eventBus 自己实现的 PendingPostQueue
Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
});
break;
case BACKGROUND://子线程
if (isMainThread) {//当前是主线程 newCachedThreadPool线程池执行
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
});
} else {//不是主线程 直接执行
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
break;
case ASYNC://异步 newCachedThreadPool线程池执行
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeSubscriber(subscription, event);
}
});
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown thread mode: " + subscription.subscriberMethod.threadMode);
}
}
private void invokeSubscriber(Subscription subscription, Object event) {
try {
subscription.subscriberMethod.method.invoke(subscription.subscriber, event);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void unregister(Object subscriber) {
List<Class<?>> subscribedTypes = typesBySubscriber.get(subscriber);
if (subscribedTypes != null) {
for (Class<?> eventType : subscribedTypes) {
List<Subscription> subscriptions = subscriptionsByEventType.get(eventType);
if (subscriptions != null) {
int size = subscriptions.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Subscription subscription = subscriptions.get(i);
if (subscription.subscriber == subscriber) {
subscription.active = false;
subscriptions.remove(i);
i--;
size--;
}
}
}
}
typesBySubscriber.remove(subscriber);
}
}
}
总结
EventBus使用发布者/订阅者模式实现松散耦合,简化组件之间的通信。使用简单,效率高,体积小。原理不算复杂,但是源码有非常非常多的细节处理值得我们去学习。
关注我获取更多知识或者投稿


本网站文章均为原创内容,并可随意转载,但请标明本文链接
如有任何疑问可在文章底部留言。为了防止恶意评论,本博客现已开启留言审核功能。但是博主会在后台第一时间看到您的留言,并会在第一时间对您的留言进行回复!欢迎交流!
本文链接: https://leetcode.jp/eventbus源码详细分析-手写eventbus核心代码/