本文的目的
目的在于教会大家到底如何自定义viewgroup,自定义布局和自定义测量到底如何写。很多网上随便搜搜的概念和流程图这里不再过多描述了,建议大家看本文之前,先看看基本的自定义viewgroup流程,心中有个大概即可。本文注重于实践。

viewgroup 的测量布局流程基本梳理
稍微回顾下,基本的viewgroup绘制和布局流程中的重点:
view 在onMeasure()方法中进行自我测量和保存,也就是说对于view(不是viewgroup噢)来说一定在onMeasure方法中计算出自己的尺寸并且保存下来
viewgroup实际上最终也是循环从上大小来调用子view的measure方法,注意子view的measure其实最终调用的是子view的onMeasure 方法。所以我们理解这个过程为: viewgroup循环遍历调用所有子view的onmeasure方法,利用onmeasure方法计算出来的大小,来确定这些子view最终可以占用的大小和所处的布局的位置。
measure方法是一个final方法,可以理解为做测量工作准备工作的,既然是final方法所以我们无法重写它,不需要过多关注他,因为measure最终要调用onmeasure ,这个onmeasure我们是可以重写的。要关注这个。layout和onlayout是一样的关系。
父view调用子view的layout方法的时候会把之前measure阶段确定的位置和大小都传递给子view。
对于自定义view/viewgroup来说 我们几乎只需要关注下面三种需求:
对于已有的android自带的view,我们只需要重写他的onMeasure方法即可。修改一下这个尺寸即可完成需求。
对于android系统没有的,属于我们自定义的view,比上面那个要复杂一点,要完全重写onMeasure方法。
第三种最复杂,需要重写onmeasure和onlayout2个方法,来完成一个复杂viewgroup的测量和布局。
onMeasure方法的特殊说明:
如何理解父view对子view的限制?
onMeasure的两个参数既然是父view对子view的限制,那么这个限制的值到底是哪来的呢?
实际上,父view对子view的限制绝大多数就来自于我们开发者所设置的layout开头的这些属性
比方说我们给一个imageview设置了他的layout_width和layout_height 这2个属性,那这2个属性其实就是我们开发者所期望的宽高属性,但是要注意了, 设置的这2个属性是给父view看的,实际上对于绝大多数的layout开头的属性这些属性都是设置给父view看的
为什么要给父view看?因为父view要知道这些属性以后才知道要对子view的测量加以什么限制?
到底是不限制(UNSPECIFIED)?还是限制个最大值(AT_MOST),让子view不超过这个值?还是直接限制死,我让你是多少就得是多少(EXACTLY)。
自定义一个BannerImageView 修改onMeasure方法
所谓bannerImageview,就是很多电商其实都会放广告图,这个广告图的宽高比都是可变的,我们在日常开发过程中也会经常接触到这种需求:imageview的宽高比 在高保真中都标注出来,但是考虑到很多手机的屏幕宽度或者高度都不确定所以我们通常都要手动来计算出这个imageview高度或者宽度,然后动态改变width或者height的值。这种方法可用但是很麻烦这里给出一个自定义的imageview,通过设置一个ratio的属性即可动态的设置iv的高度。很是方便

看下效果

最后看下代码,重要的部分都写在注释里了,不再过多讲了。
public class BannerImageView extends ImageView {
//宽高比
float ratio;
public BannerImageView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public BannerImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.BannerImageView);
ratio = typedArray.getFloat(R.styleable.BannerImageView_ratio, 1.0f);
typedArray.recycle();
}
public BannerImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//人家自己的测量还是要自己走一遍的,因为这个方法内部会调用setMeasuredDimension方法来保存测量结果了
//只有保存了以后 我们才能取得这个测量结果 否则你下面是取不到的
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//取测量结果
int mWidth = getMeasuredWidth();
int mHeight = (int) (mWidth * ratio);
//保存了以后,父view就可以拿到这个测量的宽高了。不保存是拿不到的噢。
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
}
}
自定义view,完全自己写onMeasure方法
首先明确一个结论:
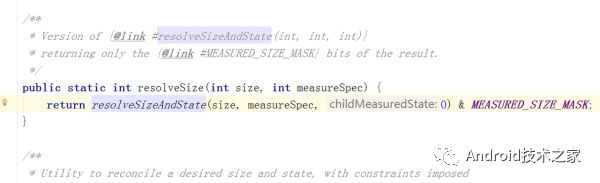
对于完全自定义的view,完全自己写的onMeasure方法来说,你保存的宽高必须要符合父view的限制,否则会发生bug,保存父view对子view的限制的方法也很简单直接调用resolveSize方法即可。

所以对于完全自定义的view onMeasure方法也不难写了,
先算自己想要的宽高,比如你画了个圆,那么宽高就肯定是半径的两倍大小, 要是圆下面还有字,那么高度肯定除了半径的两倍还要有字体的大小。对吧。很简单。这个纯看你自定义view是啥样的
算完自己想要的宽高以后 直接拿resolveSize 方法处理一下 即可。
最后setMeasuredDimension 保存。
范例:
public class LoadingView extends View {
//圆形的半径
int radius;
//圆形外部矩形rect的起点
int left = 10, top = 30;
Paint mPaint = new Paint();
public LoadingView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public LoadingView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.LoadingView);
radius = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.LoadingView_radius, 0);
}
public LoadingView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int width = left + radius * 2;
int height = top + radius * 2;
//一定要用resolveSize方法来格式化一下你的view宽高噢,否则遇到某些layout的时候一定会出现奇怪的bug的。
//因为不用这个 你就完全没有父view的感受了 最后强调一遍
width = resolveSize(width, widthMeasureSpec);
height = resolveSize(height, heightMeasureSpec);
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
RectF oval = new RectF(left, top,
left + radius * 2, top + radius * 2);
mPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
canvas.drawRect(oval, mPaint);
//先画圆弧
mPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mPaint.setStrokeWidth(2);
canvas.drawArc(oval, -90, 360, false, mPaint);
}
}
布局文件:
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width=“200dp”
android:layout_height=“200dp”
android:background=“#000000”
android:orientation=“horizontal”>
<com.example.a16040657.customviewtest.LoadingView
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:src=“@mipmap/dly”
app:radius=“200”></com.example.a16040657.customviewtest.LoadingView>
<com.example.a16040657.customviewtest.LoadingView
android:layout_marginLeft=“10dp”
android:layout_width=“wrap_content”
android:layout_height=“wrap_content”
android:src=“@mipmap/dly”
app:radius=“200”></com.example.a16040657.customviewtest.LoadingView>
</LinearLayout>
最后效果:

自定义一个viewgroup
这个其实也就是稍微复杂了一点,但是还是有迹可循的,只是稍微需要一点额外的耐心。
自定义一个viewgroup 需要注意的点如下:
一定是先重写onMeasure确定子view的宽高和自己的宽高以后 才可以继续写onlayout 对这些子view进行布局噢~~
viewgroup 的onMeasure其实就是遍历自己的view 对自己的每一个子view进行measure,绝大多数时候对子view的 measure都可以直接用 measureChild()这个方法来替代,简化我们的写法,如果你的viewgroup很复杂的话无法就是自己写一遍measureChild 而不是调用measureChild 罢了。
计算出viewgroup自己的尺寸并且保存,保存的方法还是哪个setMeasuredDimension 不要忘记了
逼不得已要重写measureChild方法的时候,其实也不难无非就是对父view的测量和子view的测量 做一个取舍关系而已,你看懂了基础的measureChild方法,以后就肯定会写自己的复杂的measureChild方法了。
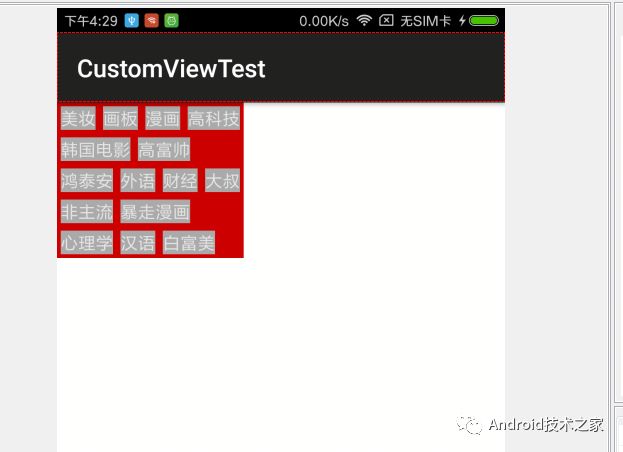
下面是一个极简的例子,一个很简单的flowlayout的实现,没有对margin paddding做处理,也假设了每一个tag的高度是固定的,可以说是极为简单了,但是麻雀虽小 五脏俱全,足够你们好好理解自定义viewgroup的关键点了。
/**
* 写一个简单的flowlayout 从左到右的简单layout,如果宽度不够放 就直接另起一行layout
* 这个类似的开源控件有很多,有很多写的出色的,我这里只仅仅实现一个初级的flowlayout
* 也是最简单的,目的是为了理解自定义viewgroup的关键核心点。
* <p>
* 比方说这里并没有对padding或者margin做特殊处理,你们自己写viewgroup的时候 记得把这些属性的处理都加上
* 否则一旦有人用了这些属性 发现没有生效就比较难看了。。。。。。
*/
public class SimpleFlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
public SimpleFlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public SimpleFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public SimpleFlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
/**
* layout的算法 其实就是 不够放剩下一行 那另外放一行 这个过程一定要自己写一遍才能体会,
* 个人有个人的写法,说不定你的写法比开源的项目还要好
* 其实也没什么夸张的,无法就是前面onMeasure结束以后 你可以拿到所有子view和自己的 测量宽高 然后就算呗
*
* @param changed
* @param l
* @param t
* @param r
* @param b
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childTop = 0;
int childLeft = 0;
int childRight = 0;
int childBottom = 0;
//已使用 width
int usedWidth = 0;
//customlayout 自己可使用的宽度
int layoutWidth = getMeasuredWidth();
Log.v(“wuyue”, “layoutWidth==” + layoutWidth);
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
//取得这个子view要求的宽度和高度
int childWidth = childView.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
//如果宽度不够了 就另外启动一行
if (layoutWidth – usedWidth < childWidth) {
childLeft = 0;
usedWidth = 0;
childTop += childHeight;
childRight = childWidth;
childBottom = childTop + childHeight;
childView.layout(0, childTop, childRight, childBottom);
usedWidth = usedWidth + childWidth;
childLeft = childWidth;
continue;
}
childRight = childLeft + childWidth;
childBottom = childTop + childHeight;
childView.layout(childLeft, childTop, childRight, childBottom);
childLeft = childLeft + childWidth;
usedWidth = usedWidth + childWidth;
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//先取出SimpleFlowLayout的父view 对SimpleFlowLayout 的测量限制 这一步很重要噢。
//你只有知道自己的宽高 才能限制你子view的宽高
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int usedWidth = 0; //已使用的宽度
int remaining = 0; //剩余可用宽度
int totalHeight = 0; //总高度
int lineHeight = 0; //当前行高
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
LayoutParams lp = childView.getLayoutParams();
//先测量子view
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//然后计算一下宽度里面 还有多少是可用的 也就是剩余可用宽度
remaining = widthSize – usedWidth;
//如果一行不够放了,也就是说这个子view测量的宽度 大于 这一行 剩下的宽度的时候 我们就要另外启一行了
if (childView.getMeasuredWidth() > remaining) {
//另外启动一行的时候,使用过的宽度 当然要设置为0
usedWidth = 0;
//另外启动一行了 我们的总高度也要加一下,不然高度就不对了
totalHeight = totalHeight + lineHeight;
}
//已使用 width 进行 累加
usedWidth = usedWidth + childView.getMeasuredWidth();
//当前 view 的高度
lineHeight = childView.getMeasuredHeight();
}
//如果SimpleFlowLayout 的高度 为wrap cotent的时候 才用我们叠加的高度,否则,我们当然用父view对如果SimpleFlowLayout 限制的高度
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
heightSize = totalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, heightSize);
}
}
最后看下效果

喜欢 就关注吧,欢迎投稿!

本网站文章均为原创内容,并可随意转载,但请标明本文链接
如有任何疑问可在文章底部留言。为了防止恶意评论,本博客现已开启留言审核功能。但是博主会在后台第一时间看到您的留言,并会在第一时间对您的留言进行回复!欢迎交流!
本文链接: https://leetcode.jp/一篇文章搞懂android-自定义viewgroup的难点/